If you need to raise FFL & DFL and you worries about breaking things here are couple suggestions and bit more break down to make better understanding about Domain and forest functional levels.
Problems may raise up : make sure you do not have any NT4.0 , Win 2000 and 2003 Domain controllers in your environment. If you do the worst case you can move the services on these DC’s to Win08 DC’s and get them out peacefully or forcefully from your active directory.
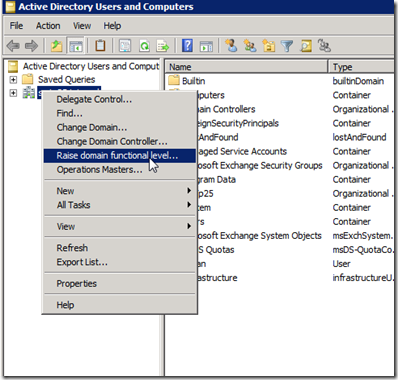
Remember : Raising the domain and forest functional levels are one-way task once it has been done going back not supported except Rebuild the domain or forest or restore it from a backup !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
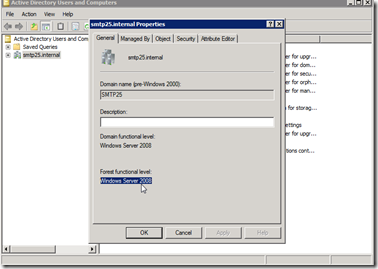
What to watch out: In reality raising DFL FFL is DC to DC task and there should be none or rare application dependency performing such task. As always if you are concern big time and yet you are not sure, build LAB environment with problem application and test your scenario to make sure you are not going to introduce additional problem. Remember if you need to go back , you have to restore your entire Forest/Domain from backup which will be biggest nightmare ever (-:
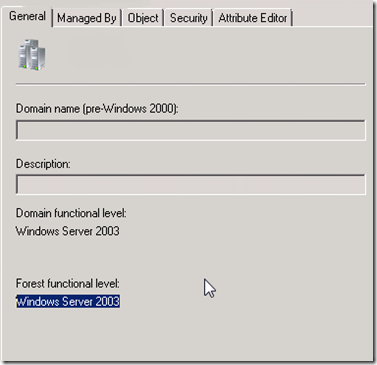
Upgrading functional levels in a new Windows Server 2008 forest
When you install the first domain controller in a new Windows Server 2008 forest, functional levels are set by default to the following levels, and they remain at these levels until you raise them manually:
- Windows 2000 native domain functional level
- Windows 2000 forest functional level
Functional levels are set at these default levels to give you the option of adding Windows Server 2003–based domain controllers to your new Windows Server 2008 R2 forest. After you create a forest root domain, the domain functional level for each domain that you add to the Windows Server 2008 R2 forest is set to Windows Server 2003. However, if you want all domain controllers in your new Windows Server 2008 R2 environment to run Windows Server 2008 R2, set the forest functional level, and then the domain functional level, to Windows Server 2008 R2 when you install the first domain controller in your forest. Doing this saves time and enables all forest-level and domain-level features in Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008
All of the default AD DS features, all of the features from the Windows Server 2003 domain functional level, and the following features are available:
- Distributed File System (DFS) replication support for the Windows Server 2003 System Volume (SYSVOL)
DFS replication support provides more robust and detailed replication of SYSVOL contents. - Some Access Based Enumeration (ABE) functionality on DFS File servers that run Windows Server 2008.
AD DS is not required for standalone DFS namespaces to support ABE. But for domain-based namespaces, use the Windows Server 2008 mode namespace, which requires the following: - Windows Server 2003 forest functional level
- Windows Server 2008 domain functional level
For more information, see Choose a Namespace Type (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=180400). - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES 128 and AES 256) support for the Kerberos protocol
- Last Interactive Logon Information
Last Interactive Logon Information displays the following information: - The total number of failed logon attempts at a domain-joined Windows Server 2008 server or a Windows Vista workstation
- The total number of failed logon attempts after a successful logon to a Windows Server 2008 server or a Windows Vista workstation
- The time of the last failed logon attempt at a Windows Server 2008 or a Windows Vista workstation
- The time of the last successful logon attempt at a Windows Server 2008 server or a Windows Vista workstation
For more information, see Active Directory Domain Services: Last Interactive Logon (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=180387). - Fine-grained password policies
Fine-grained password policies make it possible for you to specify password and account lockout policies for users and global security groups in a domain. For more information, see Step-by-Step Guide for Fine-Grained Password and Account Lockout Policy Configuration (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=91477). - Personal Virtual Desktops
To use the added functionality provided by the Personal Virtual Desktop tab in the User Account Properties dialog box in Active Directory Users and Computers, your AD DS schema must be extended for Windows Server 2008 R2 (schema object version = 47). For more information, see Deploying Personal Virtual Desktops by Using RemoteApp and Desktop Connection Step-by-Step Guide (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=183552).
Windows Server 2008 R2
All default Active Directory features, all features from the Windows Server 2008 domain functional level, plus the following features:
- Authentication mechanism assurance, which packages information about the type of logon method (smart card or user name/password) that is used to authenticate domain users inside each user’s Kerberos token. When this feature is enabled in a network environment that has deployed a federated identity management infrastructure, such as Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), the information in the token can then be extracted whenever a user attempts to access any claims-aware application that has been developed to determine authorization based on a user’s logon method.
- Automatic SPN management for services running on a particular computer under the context of a Managed Service Account when the name or DNS host name of the machine account changes. For more information about Managed Service Accounts, see Service Accounts Step-by-Step Guide (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=180401).
Respectfully,
Oz Casey, Dedeal
MVP Exchange Server
MCITP (EMA), MCITP (SA)
MCSE 2003, M+, S+, MCDST
Security+, Project +, Server +
http://smtp25.blogspot.com/ (Blog)
http://telnet25.wordpress.com/ (Blog)